In work package two (Protocols) administrative metadata from a Safe Setting at the Australian Data Archive (ADA) has been interlinked with the scholarly graph developed by Research Graph Foundation and enhanced using their Augment API. This exercise was undertaken to understand how existing metadata that incorporates Persistent IDentifiers (PID) can be associated with more information useful in risk assessments for access to sensitive research data using the CADRE Five Safes framework.
The Research Graph Foundation specialises in developing technical and informatics capabilities; transforming disconnected and siloed research activities into a connected network of scholarly works. The Foundation worked with the ADA team to augment 1,599 metadata records of datasets that are managed by the Australian Data Archive.
The augmentation process benefited from the ADA Dataverse API call to pull out the lists of datasets. The Foundation technical team then used this list to identify the ADA datasets in the Research Graph network. The record of the ADA dataset was augmented with related metadata from other data sources, including connections to publications, researchers and other datasets.
The Augment API leverages the Research Graph distributed network and persistent identifiers to establish connections between publications, researchers, research datasets and grants, across global infrastructures such as DataCite and open access initiatives such as Scholix.
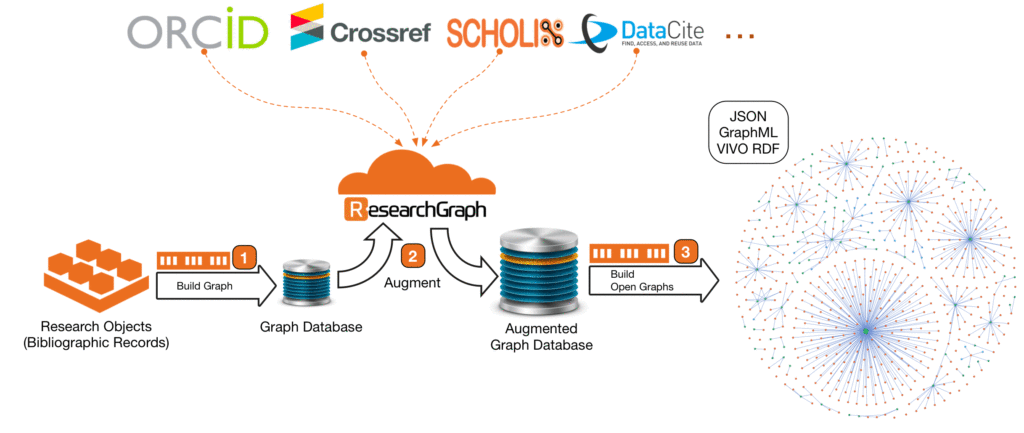
Source: Research Graph.
Research Graph Augment API is a RESTful API that transforms metadata of research objects into a collaboration network. The API transforms a single Open Researcher and Contributor ID (ORCiD) or Digital Object Identifier (DOI) to a connected graph consist of the following connections (Figure 1). For details related to the nodes in the Research Graph refer to Research Graph Schema (Figure 2).
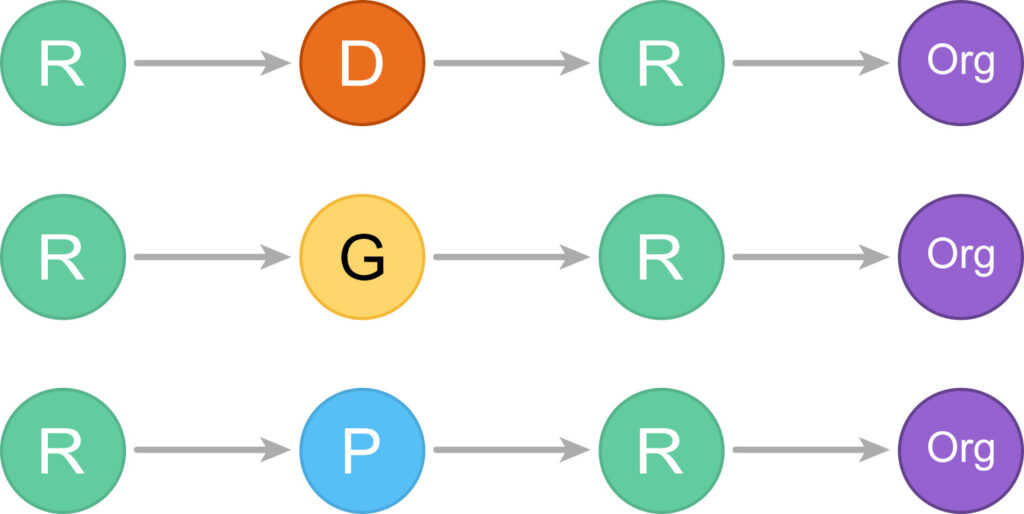
Source: Augment-API – Research Graph
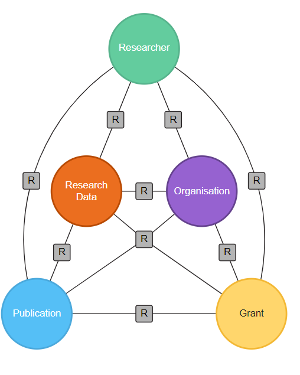
Source: ResearchGraph Schema
The graphs visualisation (Figure 3) demonstrates how ADA original graph can be augmented with metadata from ORCiD DataCite, ARCPubMed, and other registries. The ADA original graph included a total of 2,543 nodes increased to 41,896 nodes post-augmentation (Figure 4). Similarly, the total number of DOIs connected to ADA nodes significantly increased from 1,599 before augmentation to 21,699 after augmentation. Of all the metadata sources, ORCiD and Crossref were the two which contained the most metadata for publications with 19,195 and 9,749 nodes, respectively. These two PIDs also made up for most of the new nodes in the augmented ADA graph by accounting for the publication and researcher nodes as well as most of the newly augmented DOIs.
The use of the Research Graph Augment API with administrative metadata from a Safe Setting provides significant benefits by transforming disconnected data description and administrative records to a complex scholarly graph.
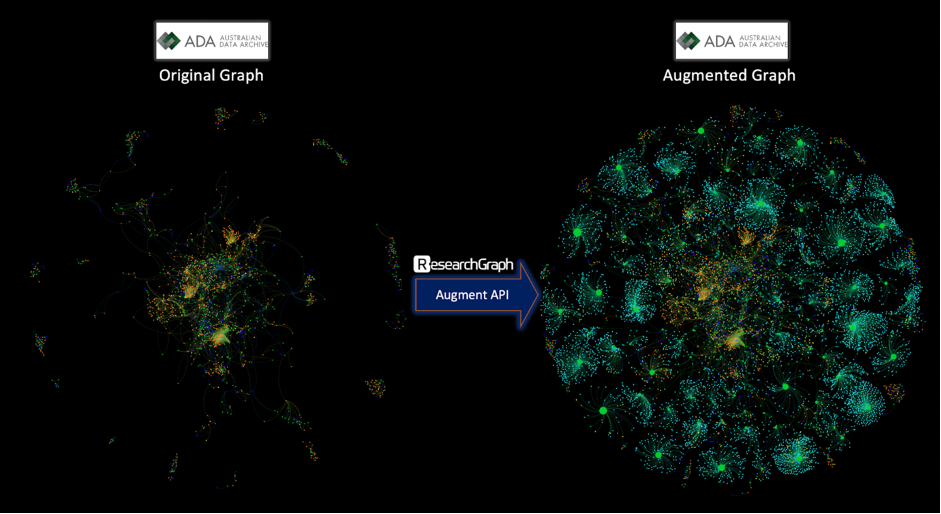
Key: orange = datasets; blue = publications, green = researchers
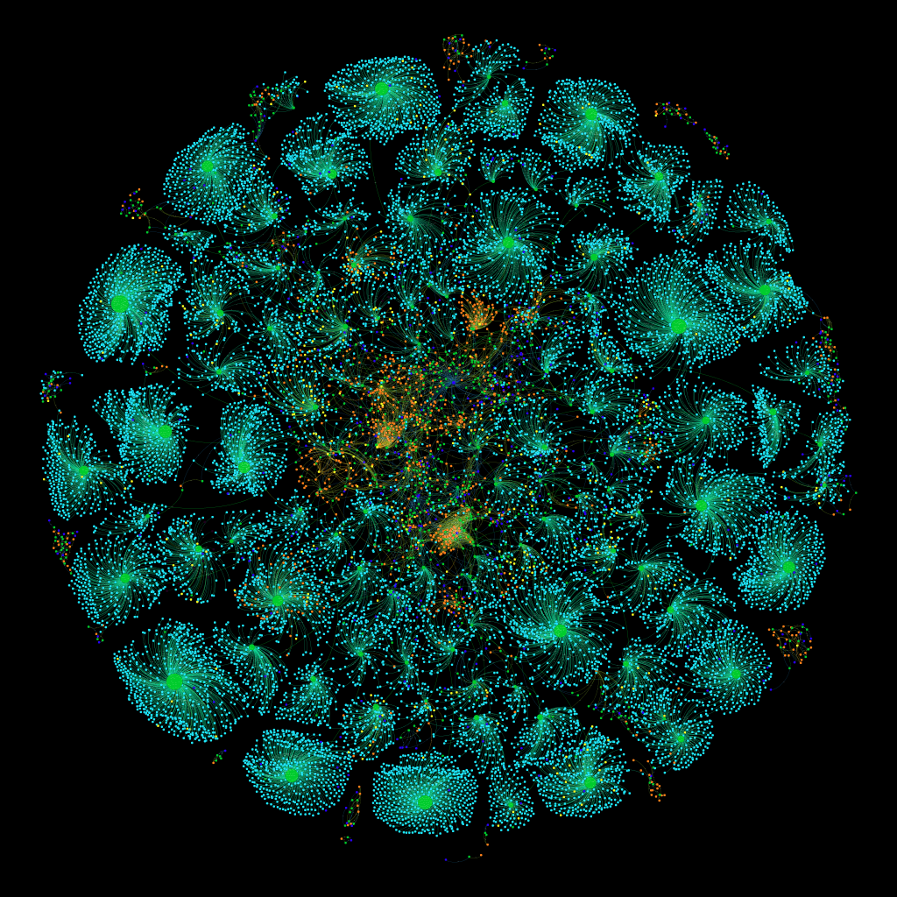
Source: Research Graph and ADA – augmentation with cross reference
Image credit: Where are you now baby blue Tim cc-by-nd 2.0

